3004 Aluminum Plate Sheet
Standards: ASTM B209/EN 485-2 and so on Strictly Control Product Quality
3004 aluminum is an alloy with aluminum as the main component and a small amount of other elements added to enhance its performance. It belongs to the 3xxx series of aluminum alloys, known for its excellent formability, corrosion resistance, and moderate strength.

3004 Aluminum Plate Advantages
- 1. Excellent corrosion resistance.
- 2. Adding a small amount of magnesium can improve strength.
- 3. Excellent machinability.
- 4. Good weldability.
| Property | Description |
| Machinability | Good machinability in the hardened state; oil-based lubricants can be used for machining operations. |
| Formability | Can be formed using traditional hot or cold working methods. |
| Weldability | Can be welded using TIG or MIG welding techniques. |
| Heat Treatment | Non-heat treatable alloy. |
| Forging | Forging temperature range is 372 to 510°C (700 to 950°F). |
| Hot Working | Can be hot worked between 260 to 483°C (500 to 900°F). |
| Cold Working | Can be cold worked using traditional techniques until a 75% reduction in area; annealing is required if reduction exceeds 75%. |
| Annealing | Anneal at 344°C (650°F) followed by air cooling. |
| Hardening | Can be hardened through cold working. |
| Applications | Used in metal sheet processing and manufacturing of storage tanks. |
3004 aluminum plate is the most popular temper
-
3004 h19 Aluminum Plate Sheet
3004 H19 is a non-heat treatable aluminum alloy suitable for chemical and food contact applications, common ones such as beverage cans.
-
3004 h18 Aluminum Plate Sheet
3004-H18 aluminum is 3004 aluminum in the H18 state, which has higher strength, excellent formability and good corrosion resistance than 3003.
-
3004 o Aluminum Plate Sheet
3004-O aluminum is 3004 aluminum in the annealed condition. It has the lowest strength and highest ductility compared to other variants of 3004 aluminum.
3004 Aluminum Plate Properties
- 1. High plasticity. 3004 aluminum plate has high plasticity in the annealed state, good plasticity in the semi-cold hardening state, and occasional plasticity in the cold hardening state.
- 2. Good processability. It can adapt to the maximum speed that most machines and equipment can reach for milling, engraving, design and other mechanical processing. In addition, 3004 aluminum plate has good weldability, but poor processability.
- 3. Slightly higher strength. Due to the addition of alloying element Mn, 3004 aluminum plate has slightly improved strength while maintaining the excellent processing performance and corrosion resistance of natural aluminum, which is better than 3003 aluminum plate and about 10% higher than 1100 series.
- 4. Good anodizing, the surface corrosion resistance of 3004 aluminum plate after anodizing is enhanced, and it can also present colorful tones.
Aluminum 3004 Data Sheet
3004 Aluminum Plate Sheet Specifications
- Widths: Usually available in a variety of widths, from a few inches to a few feet. Common widths include 36", 48", and 60".
- Lengths: Usually available in standard lengths such as 96 inches (8 feet) or 120 inches (10 feet). Custom lengths are also available.
- Typical Sizes: Typically available in standard sizes of 4 feet by 8 feet (48 inches by 96 inches) or 4 feet by 10 feet (48 inches by 120 inches).
3004 Aluminum Plate Sheet Thickness
Common Thicknesses: Typical thicknesses range from 0.016" (0.4mm) to 0.25" (6.35mm) and thicker, depending on specific requirements.
3004 Aluminum Plate Surface Treatment
3004 aluminum sheet can be given a variety of finishes such as burnished (a natural aluminum finish), anodized (to enhance corrosion resistance and provide decorative options), painted, or coated.
Typical Mechanical Properties Data Of Aluminum 3004
| Alloy-Temper | 3004-O | 3004-H34 | 3004-H38 | |
| Tensile Strength | (ksi) | 26 | 39 | 41 |
| Yield Strength | (ksi) | 10 | 29 | 36 |
| Elongation | (%) | 19 | 5 | 4 |
Aluminum Alloy al 3004 Melting Point
Like most aluminum alloys, 3004 aluminum alloy has a melting point of about 660 degrees Celsius or 1220 degrees Fahrenheit. This temperature represents the point at which a solid alloy transitions to a liquid state during heating. It's worth noting that the melting point will vary slightly depending on the exact components and impurities in the alloy, but 660 degrees Celsius is typical for aluminum alloys.

3004 Aluminum Plate Standards
- ASTM B 209: Standard Specification for Aluminum and Aluminum Alloy Sheets
- ASTM B 221: Standard Specification for Aluminum and Aluminum Alloy Extruded Rods, Rods, Wire, Shapes, and Tubes
- ASTM B 547: Standard Specification for Formed and Arc-Welded Circular Tubing of Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys
- ISO 6361: Wrought aluminum and aluminum alloy sheet, strip, and plate
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials)
- International standards such as EN (European Norms)
3004 Aluminum Plate Certified
Depending on the manufacturer and specific application, e.g. ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems), or specific industry certifications related to automotive, construction, or other applications.
3004 Aluminum Sheet may come with certifications such as Mill Test Report (MTR) or Certificate of Compliance to ensure the quality and compliance of the product.
Equivalent to 3004 Aluminum
Some alternative names for 3004 aluminum include AA3004, EN AW-3004, AW-3004, AlMn1Mg1, 3.0526, and A93004, among others.
However, specific specifications, mechanical properties, and chemical composition may vary slightly by manufacturer and specific production process. Therefore, it is advisable to consult the manufacturer or supplier for accurate information about the 3004 aluminum sheet you need.
3004 Aluminum Plate Composition
Chemical composition: The chemical composition of 3004 aluminum alloy usually has aluminum (Al) as the main element, manganese (Mn), and magnesium (Mg) as the main alloying elements. The approximate chemical composition of 3004 aluminum alloy is as follows:
- Aluminum (Al): 95.7 - 98.8%
- Manganese (Mn): 1.0 - 1.5%
- Magnesium (Mg): 0.8 - 1.3%
- Other elements (each): ≤0.05%
- Other elements (total): ≤0.15%
- Impurities: ≤0.15%
Mechanical Properties
| Properties | Metric | Imperial |
| Tensile strength | 215 MPa | 31183 psi |
| Yield strength | 170 MPa | 24656 psi |
| Shear strength | 115 MPa | 16680 psi |
| Fatigue strength | 105 MPa | 15229 psi |
| Elastic modulus | 70-80 GPa | 10153-11603 ksi |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| Elongation | 10% | 10% |
| Hardness | 52 | 52 |
| Temper | Specified Thickness(in) | Tensile Strength - KSI | Elongationin 2 inches % | |||
| Ultimate | Yield | |||||
| Min | Max | Min | Max | |||
| H12 | 0.008 - 0.020 | 27.6 | 34.8 | - | - | 2 |
| H12 | 0.020 - 0.059 | 27.6 | 34.8 | - | - | 3 |
| H12 | 0.059 - 0.118 | 27.6 | 34.8 | - | - | 4 |
| H12 | 0.118 - 0.236 | 27.6 | 34.8 | - | - | 5 |
| H12 | 0.236 - 0.394 | 27.6 | 34.8 | - | - | - |
| H14 | 0.008 - 0.020 | 31.9 | 38.4 | - | - | 1 |
| H14 | 0.020 - 0.059 | 31.9 | 38.4 | - | - | 2 |
| H14 | 0.059 - 0.118 | 31.9 | 38.4 | - | - | 2 |
| H14 | 0.118 - 0.250 | 31.9 | 38.4 | - | - | 3 |
| H16 | 0.008 - 0.020 | 34.8 | 41.3 | - | - | 1 |
| H16 | 0.020 - 0.059 | 34.8 | 41.3 | - | - | 1 |
| H16 | 0.059 - 0.118 | 34.8 | 41.3 | - | - | 2 |
| H16 | 0.118 - 0.250 | 34.8 | 41.3 | - | - | 2 |
| H18 | 0.008 - 0.020 | 37.7 | - | - | - | 1 |
| H18 | 0.020 - 0.059 | 37.7 | - | - | - | 1 |
| H18 | 0.059 - 0.118 | 37.7 | - | - | - | - |
| H18 | 0.118 - 0.250 | 37.7 | - | - | - | - |
| H19 | 0.008 - 0.020 | 39.2 | - | - | - | 1 |
| H19 | 0.020 - 0.059 | 39.2 | - | - | - | 1 |
| H19 | 0.059 - 0.118 | 39.2 | - | - | - | - |
| H19 | 0.118 - 0.250 | 39.2 | - | - | - | - |
| H22/32 | 0.008 - 0.020 | 27.6 | 34.8 | - | - | 4 |
| H22/32 | 0.020 - 0.059 | 27.6 | 34.8 | - | - | 5 |
| H22/32 | 0.059 - 0.118 | 27.6 | 34.8 | - | - | 6 |
| H22/32 | 0.118 - 0.250 | 27.6 | 34.8 | - | - | 7 |
| H22/32 | 0.236 - 0.394 | 27.6 | 34.8 | - | - | - |
| H24/34 | 0.008 - 0.020 | 31.9 | 38.4 | - | - | 3 |
| H24/34 | 0.020 - 0.059 | 31.9 | 38.4 | - | - | 4 |
| H24/34 | 0.059 - 0.118 | 31.9 | 38.4 | - | - | 4 |
| H24/34 | 0.118 - 0.250 | 31.9 | 38.4 | - | - | - |
| H26/36 | 0.008 - 0.020 | 34.8 | 41.3 | - | - | 3 |
| H26/36 | 0.020 - 0.059 | 34.8 | 41.3 | - | - | 3 |
| H26/36 | 0.059 - 0.118 | 34.8 | 41.3 | - | - | 3 |
| H26/36 | 0.118 - 0.250 | 34.8 | 41.3 | - | - | - |
| H28/38 | 0.008 - 0.020 | 37.7 | - | - | - | 2 |
| H28/38 | 0.020 - 0.059 | 37.7 | - | - | - | 3 |
| H28/38 | 0.059 - 0.118 | 37.7 | - | - | - | - |
| H28/38 | 0.118 - 0.250 | 37.7 | - | - | - | - |
| O/H111 | 0.008 - 0.020 | 22.5 | 29 | - | - | 13 |
| O/H111 | 0.020 - 0.059 | 22.5 | 29 | - | - | 14 |
| O/H111 | 0.059 - 0.118 | 22.5 | 29 | - | - | 15 |
| O/H111 | 0.118 - 0.250 | 22.5 | 29 | - | - | 16 |
Thermal Properties
| Thermal Properties | Original Value | Comments |
| CTE, linear | 13.3 µin/in-°F @Temperature 20.0 - 100 °C | AA; Typical; average over range |
| 21.5 µm/m-°C @Temperature -50.0 - 20.0 °C | ||
| 23.2 µm/m-°C @Temperature 20.0 - 100 °C | ||
| 24.1 µm/m-°C @Temperature 20.0 - 200 °C | ||
| 25.1 µm/m-°C @Temperature 20.0 - 300 °C | ||
| Specific Heat Capacity | 0.893 J/g-°C | |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1130 BTU-in/hr-ft²-°F | AA; Typical at 77°F |
| Melting Point | 1165 - 1210 °F | AA; Typical range based on typical composition for wrought products >= 1/4 in. thickness |
| Solidus | 1165 °F | AA; Typical |
| Liquidus | 1210 °F | AA; Typical |
Bend radii
| Recommended Minimum Bend Radii for 90-Degree Cold Forming of Sheet of 3004 (Reference test method – ASTM E290) Thickness (t) | |||||
| Temper | 1.6mm | 3.2mm | 4.8mm | 6.0mm | 10mm |
| 0 | 0t | ½t | 1t | 1t | 1t |
| H32 | ½t | 1t | 1t | 1½t | 1½t |
| H34 | 1t | 1½t | 1½t | 2½t | 2½t |
| H36 | 1½t | 2½t | 3t | 3½t | 4t |
| H38 | 2½t | 3t | 4t | 5t | 5½t |
Is Aluminum 3004 Strong?
Aluminum alloy 3004 is not typically considered a high-strength aluminum alloy when compared to other aluminum alloys, such as 2024 or 7075, which are known for their exceptional strength. Instead, 3004 is characterized as a moderate-strength alloy.
The strength of aluminum alloy 3004 can be influenced by factors such as its temper condition. In the H18 temper, which signifies that the aluminum has undergone strain hardening, 3004 will have moderately higher strength compared to the annealed (O) condition but is still not as strong as some other temper conditions like H14 or H24.
The primary attributes of 3004 alloy include its excellent formability and corrosion resistance, rather than its strength. It is often used in applications where moderate strength is sufficient, and other properties like ductility, weldability, and resistance to corrosion are more critical.
In summary, while aluminum alloy 3004 is not known for its high strength, it can meet the requirements of applications that prioritize other properties, such as formability and corrosion resistance, over sheer strength. The choice of alloy should be based on the specific needs of the intended application.
What is 3004 Aluminum Used for?
3004 aluminum plate refers to a flat aluminum plate made of 3004 alloy. It is commonly used in various industries requiring lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant materials. Some typical uses for 3004 aluminum sheet include:
| Application | Description |
| Beverage Cans | 3004 aluminum alloy is commonly used for manufacturing beverage cans due to its good formability and corrosion resistance. It can easily be formed into sheet metal for can bodies and maintains stability under various environmental conditions. |
| Food Cans | Similar to beverage cans, 3004 aluminum alloy is used for making food cans, such as baby food containers and canned goods, due to its compliance with food safety requirements and corrosion resistance. |
| Automotive Body Panels | 3004 aluminum alloy, with excellent formability and strength, is also used for manufacturing automotive body panels. It provides sufficient strength to protect the vehicle structure while reducing overall vehicle weight, contributing to improved fuel efficiency. |
| Aluminum Roofing Sheets | Used in the production of roofing sheets, 3004 aluminum alloy's corrosion resistance makes it highly suitable for outdoor environments. |
| Household Appliances | Due to its good formability, 3004 aluminum alloy is widely used in the manufacturing of household appliances such as tubs for washing machines, refrigerator liners, etc. |
| Decorative Building Materials | 3004 aluminum alloy is utilized for indoor and outdoor decorative building materials such as ceilings, wall panels, and decorative facades. Its surface can be painted or coated to achieve various colors and textures. |
| Other Applications | Besides the mentioned applications, 3004 aluminum alloy is also employed in various other fields including electronic product casings, traffic signs, shipbuilding, etc. |
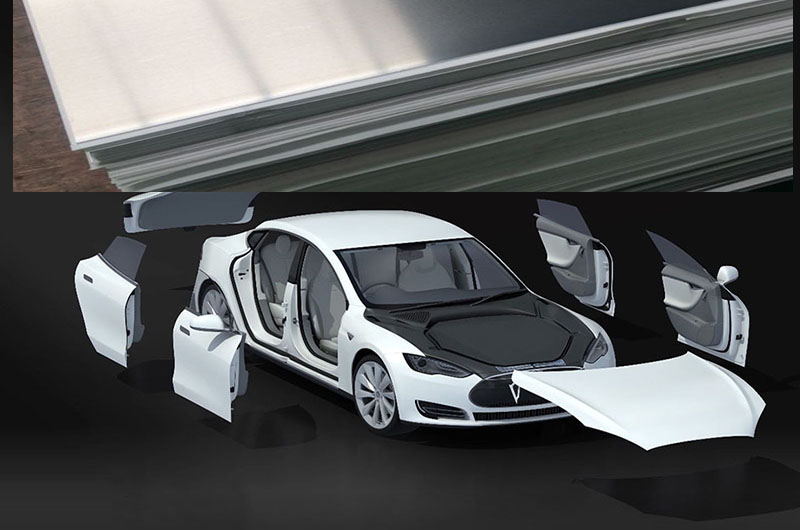
3004 Automotive Aluminum Plate
The combination of formability and corrosion resistance of 3004 alloy makes it suitable for these applications.
- Application: automotive body panels, such as hoods, fenders, trunk lids, etc.
- Temper: H14, H24
These tempers provide the alloy with a balance of strength and formability, making it suitable for forming into automotive body panels.

Architecture and Construction
Alloy 3004 can withstand harsh weather conditions and provide long-lasting performance due to its corrosion resistance.
- Applications: Roofs, siding, and other exterior components of buildings.
- Temper: H14, H24
These tempers provide good formability while maintaining adequate strength and corrosion resistance.
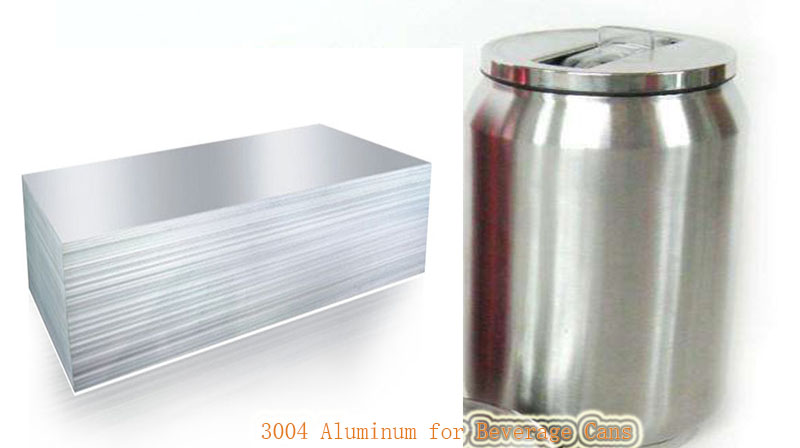
3004 Aluminum for Beverage Cans
Alloy 3004 is widely used in the production of beverage cans and has good formability, making it suitable for high-speed canning operations.
- These sheets are formed into can bodies or ends
- Plates used in beverage can manufacturing are usually in the H19 temper.
This state provides the alloy with high strength and excellent formability, enabling an efficient production process.

Chemical Equipment
The corrosion resistance of 3004 aluminum alloy ensures the safe storage and transportation of various chemicals.
- Application site: Construction of chemical storage tanks, pipelines, and other equipment.
- Temper: H32, H34
These tempered states provide the alloy with increased strength and corrosion resistance, ensuring the durability and integrity of the equipment.
Heat Exchanger
The formability and thermal conductivity of 3004 aluminum make it suitable for heat exchanger applications. These sheets can be made into complex shapes, allowing efficient heat transfer.
For heat exchanger applications, a 3004 aluminum plate is usually available in the H34 or H38 temper. These tempering conditions provide the combination of strength and formability required for effective heat transfer and structural integrity.
3004 aluminum plate is available in various thicknesses, widths, and lengths depending on the specific requirements of the application. They can be further processed by cutting, bending, or welding to the required size and shape.
When considering a 3004 aluminum plate, it is essential to consult with the supplier or manufacturer to ensure that the specific alloy and plate specification will meet your project needs.
What is the difference between 3003 and 3004 Aluminum?
Alloy Composition
- 3003 aluminum: It is an aluminum-manganese alloy mainly composed of aluminum (about 98.6%) and manganese (about 1.2-1.5%). It also contains trace amounts of other elements such as copper, iron, and silicon.
- 3004 Aluminum: It is also an aluminum-manganese alloy, but the composition is slightly different. It consists of aluminum (approximately 95.7-98.2%), manganese (approximately 0.8-1.3%), and small amounts of other elements such as copper, iron, silicon, zinc, magnesium, titanium, and chromium.
Strength and Formability
- 3003 Aluminum: Known for its excellent formability and high ductility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications requiring complex forming and shaping. However, it has lower strength compared to 3004 aluminum.
- 3004 Aluminum: It offers higher strength than 3003 Aluminum, making it more suitable for structural applications that require greater strength and stability. While it retains good formability, it may not be as ductile as 3003 aluminum.
Solderability and Corrosion Resistance
Both 3003 and 3004 aluminum alloys have good weldability and can be easily joined by various welding methods.
In terms of corrosion resistance, both alloys exhibit good resistance to atmospheric corrosion. However, the higher manganese content in 3004 aluminum helps improve corrosion resistance in more corrosive environments compared to 3003 aluminum.
Application
- 3003 Aluminum: It is commonly used for general purposes such as cookware, cookware, heat exchangers, and various packaging materials. Its excellent formability and corrosion resistance make it popular in these industries.
- 3004 Aluminum: It is often used in applications requiring a combination of strength, formability, and corrosion resistance. Common applications include beverage cans, roofing and siding materials, chemical equipment, and parts for the automotive industry.
People also searched for Aluminum Plate
-
3003 Aluminum Plate Sheet
3003 aluminum has excellent processability, weldability, and corrosion resistance. Compared with 1100 aluminum, 3003 aluminum is approximately 20% stronger.
-
3003 h22 Aluminum Plate
3003 - H22 has good strength, high durability, easy machining, high corrosion resistance and light weight. The popular product is mainly 3003-H22 Bright Aluminum Tread Plate.
-
3003 h24 Aluminum Plate
Ensure the 3003 h24 Aluminum Plate meets the required specifications including dimensional accuracy, chemical composition, mechanical properties, and surface finish.
-
3003 O Aluminum Plate Sheet
3003 O-state aluminum plate has low hardness, and 3003 O-state aluminum plate is suitable for stamping, spinning, stretching, etc.
-
3003 h14 Aluminum Plate Sheet
3003-H14 aluminum plate has the characteristics of high strength, high durability, easy processing, strong corrosion resistance and light weight. 3003 aluminum is suitable for outdoor and harsh environment applications.
-
3104 Aluminum Plate Sheet
The performance of the 3104 aluminum plate is stable, the surface is smooth, smooth, and free of defects, and the tolerance is strictly controlled to meet the standard.
-
3104 h19 Aluminum Plate Sheet
3104 h19 Aluminum Plate Sheet has precise specifications, good shape, high strength, easy processing, and good deep drawing performance.
-
3105 Aluminum Plate Sheet
3105 aluminum alloy is stronger than 1100 and 3003 alloys. 3105 aluminum sheet is often used in street signs, building siding and bottle caps.

