3004 h18 Aluminum Plate Sheet
Smooth Surface Stable Performance
What does H18 mean in 3004 Aluminum?
In the context of 3004 aluminum, the temper designation "H18" indicates the alloy's specific heat treatment process and resulting mechanical properties.
3004-H18 aluminum is 3004 aluminum in H18 condition. This is the strongest temper usually produced by strain hardening action alone.
3004 H18 aluminum plate also belongs to the aluminum-manganese alloy series. It has higher strength, excellent formability and good corrosion resistance than 3003, and it requires parts with higher strength than 3003 alloy.

For 3004 aluminum, the H18 temper indicates that the material has been strain-hardened and subjected to a controlled annealing process. Here's what H18 means for 3004 aluminum:
- Strain hardening (H): The "H" in H18 stands for strain hardening, which involves the plastic deformation of aluminum alloys to increase their strength. For 3004 aluminum, the material is usually cold-worked by processes such as rolling or drawing to induce strain hardening.
- High Strength (18): The number "18" after the H indicates high strain hardening and high strength. H18 tempering significantly increases the mechanical strength of 3004 aluminum alloy.
3004 H18 aluminum plates are mainly used in chemical product production and storage devices, thin plate processing components, building materials, building baffles, cable ducts, sewers, various lighting components, beverage cans, corrugated plates, building materials, colored aluminum plates, and lamp heads.
Mechanical properties: Tensile strength σb (MPa): 150~285 Elongation δ10 (%): 1~16 Annealing temperature: 415℃
Properties of 3004 H18 Aluminum Plate
- Reaction with Acids: Aluminum reacts with strong acids, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl) or sulfuric acid (H2SO4), resulting in the production of hydrogen gas and the dissolution of the aluminum surface. However, in practical applications, 3004 aluminum is often coated or treated to protect it from such reactions.
- Reaction with Alkalis: Aluminum is generally resistant to alkalis, including sodium hydroxide (NaOH), at room temperature. However, prolonged exposure to strong alkalis can lead to aluminum corrosion.
- Oxidation Resistance: Aluminum alloys like 3004 are highly resistant to oxidation at normal temperatures, thanks to the formation of a naturally occurring oxide layer on their surfaces.
- Interactions with Other Metals: In contact with certain dissimilar metals (e.g., copper or steel), aluminum can experience galvanic corrosion due to differences in electrode potential. Proper insulation or coatings may be necessary to prevent galvanic corrosion in specific applications.
- Flammability: Aluminum and its alloys are non-combustible and do not support combustion. This property makes them suitable for applications where fire resistance is important.
- Chemical Stability: Aluminum alloys, including 3004, are chemically stable in many environments, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
- High Tensile Strength: The H18 temper can significantly increase the tensile strength compared to softer tempers.
- Increased hardness: H18 aluminum has a higher hardness, making it more resistant to deformation and wear.
- Reduced ductility: While the H18 temper increases strength, it may slightly reduce the ductility and formability of the alloy compared to soft tempers.
- Formability: 3004 H18 aluminum retains a reasonable level of formability, but it may require more force or specialized forming techniques than softer tempers.
- Corrosion Resistance: H18 tempering does not significantly affect the inherent corrosion resistance of 3004 aluminum.

The specific mechanical properties of 3004 H18 Aluminum, such as tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, and hardness, may vary depending on the manufacturing process and specific requirements. For accurate information on the mechanical properties of 3004 H18 Aluminum, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer or supplier.
3004 h18 Aluminum Plate General Properties
| Property | Density |
| Temperature | 23.0 °C |
| Value | 2.8 g/cm³ |
3004 h18 Aluminum Plate Mechanical Properties
| Property | Temperature | Value | Comment |
| Elastic modulus | 23.0 °C | 69 GPa | |
| Elongation | 23.0 °C | 1.2 % | |
|
Plane-Strain Fracture Toughnes |
23.0 °C | 22 - 35 MPa·√m |
Typical for Wrought 3000 Series Aluminium |
| Poisson's ratio | 23.0 °C | 0.33 [-] | Typical for Wrought 3000 Series Aluminium |
| Shear modulus | 23.0 °C | 25 - 26 GPa | Typical for Wrought 3000 Series Aluminium |
| Tensile strength | 23.0 °C | 300 MPa | |
| Yield strength | 23.0 °C | 260 MPa |

Note that these values are general ranges and may vary depending on the specific alloy composition, tempering process, and testing method. To obtain precise mechanical property data for a specific lot or supplier, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer's or supplier's specification or perform specific tests on the material
3004 h18 Aluminum Plate Thermal Properties
| Property | Temperature | Value |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | 23.0 °C | 2.4E-5 1/K |
| Melting point | 630 °C | |
| Specific heat capacity | 23.0 °C | 890 J/(kg·K) |
| Thermal conductivity | 23.0 °C | 160 W/(m·K) |
3004 H18 Aluminum Plate Electrical Properties
| Property | Electrical conductivity | Electrical resistivity |
| Temperature | 23.0 °C | 23.0 °C |
| Value | 2.30E+7 - 2.90E+7 S/m | 3.4E-8 - 4.2E-8 Ω·m |
| Comment | Typical for Wrought 3000 Series Aluminium | Typical for Wrought 3000 Series Aluminium |
3004 h18 Aluminum Plate Chemical properties
| Property | Value |
| Aluminium | 95.6 - 98.2 % |
| Copper | 0 - 0.25 % |
| Iron | 0 - 0.7 % |
| Magnesium | 0.8 - 1.3 % |
| Manganese | 1 - 1.5 % |
| Other | 0 - 0.15 % |
| Silicon | 0 - 0.3 % |
| Zinc | 0 - 0.25 % |
3004 h18 Aluminum Plate Applications
| Application | Application Detail |
|---|---|
| Automotive body panels | Hoods, fenders, doors, trunk lids |
| Building and construction | Roofing, siding, facades, architectural components |
| Beverage can ends | Can lids, precise dimensions, excellent integrity |
| Heat exchangers | Air conditioning systems, radiators, automotive cooling systems |
| Electrical enclosures | Control panels, cabinets, junction boxes |
| Industrial equipment | Storage tanks, chemical processing equipment, HVAC components |
| Kitchenware | Cookware, baking sheets, utensils |
| Signage and display | Outdoor signage, indoor displays, decorative applications |
In addition to the application of 3004 h18 aluminum mentioned earlier, it is also commonly used as the base material of aluminum honeycomb core.
The aluminum honeycomb core base material is 3004 aluminum foil, and the state is mostly h18. Its thickness is about 0.038-0.06mm. Fast, and the price is relatively cheap, so it is very popular among market users.
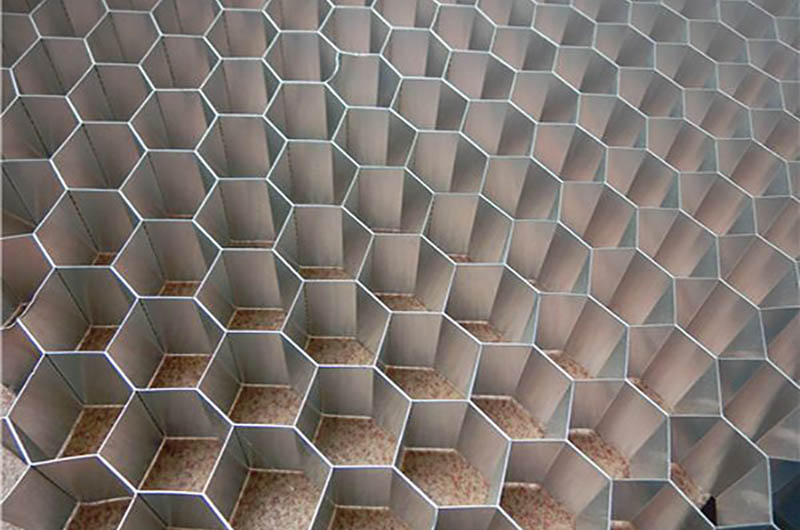
The base material of the aluminum honeycomb core can be 3003 aluminum foil, 3004 aluminum foil, 8011 aluminum foil, etc. Compared with the technical parameters, 3004 aluminum foil is more suitable for an aluminum honeycomb core. The tensile strength of 3004 aluminum foil is better than that of 3003 aluminum foil under the same thickness. And 8011 aluminum foil and 3004 aluminum foil have certain advantages in terms of elongation and cupping value.
- Lightweight, high strength, good rigidity, and series resistance.
- High-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, aging resistance.
- High flatness, good pattern, and good bonding strength.
- It has good flame retardant, sound insulation, and heat insulation effects.
- Easy to process, stable and reliable performance, strong decoration.
- The recycling rate is high, and it belongs to the green environmental protection product.
3004 h18 Aluminum Plate vs 3004 h19 Aluminum Plate
Temper Condition
H18 and H19 refer to different heat treatment conditions of aluminum sheets.
- 3004 H18: H18 indicates a high degree of strain hardening and subsequent annealing. The material is strain-hardened and then subjected to a controlled annealing process.
- 3004 H19: H19 also represents a high degree of strain hardening, but is not subjected to the same annealing process as H18. It is mainly achieved by cold working to achieve the required hardness and strength.
Strength
Tempering conditions affect the strength of the aluminum sheet.
- 3004 H18: The H18 temper provides high strength due to a combination of strain hardening and annealing. Compared with H19, it has higher tensile strength and yield strength.
- 3004 H19: The H19 temper also provides good strength, but may be slightly lower compared to H18 due to the lack of an annealing process.
Ductility and Formability
Tempering conditions affect the ductility and formability of aluminum sheets.
- 3004 H18: Due to the strain hardening and annealing process, the ductility of the H18 temper may be slightly reduced compared to H19. However, it still retains good formability for various applications.
- 3004 H19: H19 tempers generally provide higher ductility and formability than H18. It is easier to bend and form for applications requiring complex shapes or tight bends.
Application
H18 and H19 aluminum sheets have their respective applications based on their mechanical properties and formability.
- 3004 H18: The H18 plate is commonly used in applications requiring high strength and moderate formability, such as automotive body panels, building components, and heat exchangers.
- 3004 H19: The H19 plate is suitable for applications requiring excellent formability such as deep-drawn parts, can ends, and other complex shapes.
The specific mechanical properties, dimensions, and applications of 3004 H18 and H19 aluminum sheets may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer and the specific production process. It is recommended to consult the manufacturer or supplier for accurate information and availability to meet your specific project requirements.
-
3004 Aluminum Plate Sheet
3004 aluminum is similar to 3003 aluminum, but it is stronger than 3003 alloy. 3004 aluminum also has good formability, good processability, excellent corrosion resistance and drawing characteristics.
-
3004 h19 Aluminum Plate Sheet
3004 H19 is a non-heat treatable aluminum alloy suitable for chemical and food contact applications, common ones such as beverage cans.
-
3004 o Aluminum Plate Sheet
3004-O aluminum is 3004 aluminum in the annealed condition. It has the lowest strength and highest ductility compared to other variants of 3004 aluminum.
People also searched for Aluminum Plate
-
3003 Aluminum Plate Sheet
3003 aluminum has excellent processability, weldability, and corrosion resistance. Compared with 1100 aluminum, 3003 aluminum is approximately 20% stronger.
-
3003 h22 Aluminum Plate
3003 - H22 has good strength, high durability, easy machining, high corrosion resistance and light weight. The popular product is mainly 3003-H22 Bright Aluminum Tread Plate.
-
3003 h24 Aluminum Plate
Ensure the 3003 h24 Aluminum Plate meets the required specifications including dimensional accuracy, chemical composition, mechanical properties, and surface finish.
-
3003 O Aluminum Plate Sheet
3003 O-state aluminum plate has low hardness, and 3003 O-state aluminum plate is suitable for stamping, spinning, stretching, etc.
-
3003 h14 Aluminum Plate Sheet
3003-H14 aluminum plate has the characteristics of high strength, high durability, easy processing, strong corrosion resistance and light weight. 3003 aluminum is suitable for outdoor and harsh environment applications.
-
3104 Aluminum Plate Sheet
The performance of the 3104 aluminum plate is stable, the surface is smooth, smooth, and free of defects, and the tolerance is strictly controlled to meet the standard.
-
3104 h19 Aluminum Plate Sheet
3104 h19 Aluminum Plate Sheet has precise specifications, good shape, high strength, easy processing, and good deep drawing performance.
-
3105 Aluminum Plate Sheet
3105 aluminum alloy is stronger than 1100 and 3003 alloys. 3105 aluminum sheet is often used in street signs, building siding and bottle caps.

